02.03.2021
Moisture Sensitivity Levels Explained


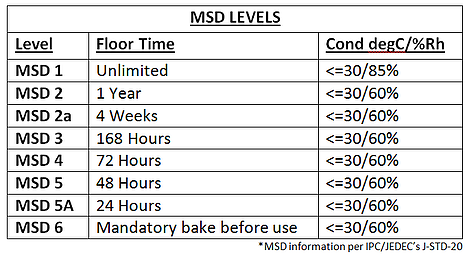
Management of moisture sensitive devices begins with understanding each devices level of sensitivity. The classification of moisture sensitive components is outlined in the IPC specification J-STD-20. Below is a basic chart which defines moisture exposures applicable to Surface Mount Device (SMD) packages.
Understand Handling and Packaging
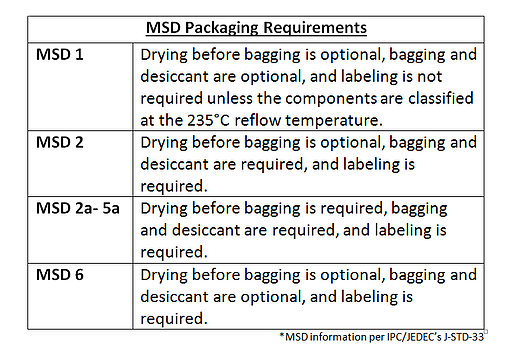
IPC J-STD-033, like all moisture sensitive precautions, focuses on prevention through appropriate packaging. In particular, moisture sensitive devices should be packaged in bags with desiccant and humidity indicators in bags with moisture barriers. The bag should have a moisture sensitive label on the exterior, ideally displaying shelf life information including max exposure after unsealing, humidity and temp ranges, and peak temperature. Baking should be seen as necessary when packaging precautions have been violated.
Understand Baking
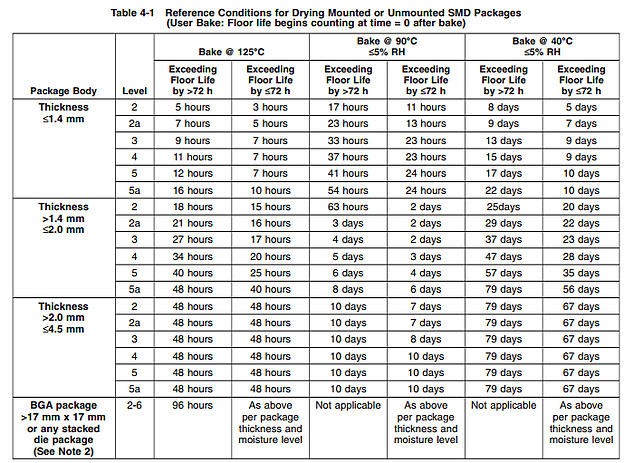
Baking of MSD components can be broken into two categories, pre-baking and post-baking. Pre-baking is used to prepare components for dry packing, while post-baking is used to recondition components after floor life expiration. You must use caution when determining the bake temperature and time, improper baking can cause poor solderability by damaging the leads through oxidation. It's important to have an understanding of proper baking temperature. Below is a J-STD-33 chart which outlines proper baking conditions.
Familiarity with the moisture sensitivity levels, as well as handling, packaging, and baking requirements of moisture sensitive SMD packages will ensure the quality and reliability of your PCBAs.
Further Reading: What Is Complementary Test for PCB Assembly?
This post originally appeared on the DigiSource Blog


